
Much has been written and researched about Artificial Intelligence. It is a technology that has now come of age. But what does it really mean and how does it work? How is it different than machine or deep learning? And how can it be used in a commercial environment to best drive business value? Given its importance in the field of data collection, analysis, and reporting, if your business depends on understanding data and acting quickly upon it, then you need to understand this technology and how it is evolving. This article will take a closer look at artificial intelligence vs. machine learning to help clarify what it is, what it isn’t, and how best to leverage it today and in the future.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
The field of artificial intelligence (AI) can point its origins to a conference that was held in 1956 at Dartmouth College, in Hanover, New Hampshire (source). Since that time, its evolution is best described as a series of breakthroughs and quiet periods as new research breakthroughs occurred and results were analyzed. The term artificial simply means “not natural or real.” According to Merriam-Webster, the term intelligence can be defined as the ability to learn or understand a new situation. Said differently, being skilled at the use of reason. Note how this definition is quite broad, nor does it suggest who or what entity does these intelligent activities, yet most assume AI is done by a computer.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the ability of a computer to simulate human thinking and understanding.
What is Machine Learning?
The use and development of computer systems that are able to learn and adapt without following explicit instructions. This is done by using algorithms and statistical models to analyze and draw inferences from patterns in data.
Oxford Dictionary
In this case, the use of computers is clearly defined – but so too is a reference to being able to learn and adapt without following explicit instructions. This sounds a lot like reasoning, doesn’t it?
In the world of data science, Artificial Intelligence is a broad term used to capture all activities performed by machines to mimic human thinking and do something smart. How do machines make these decisions? The same way that humans make decisions – just at a different scale.
An Example
Tomorrow evening you must decide what to eat for dinner. You likely have several choices, based on the data that is available to you surrounding this decision. Some factors might be how much time do you have? What food is in your house? What specials are being offered at local restaurants? Your brain processes all of these data “inputs” to come up with a decision on what to eat.
Computers can be programmed to do the same process, provided the programmers have access to all the relevant data that is most important in making this decision. Here is where it gets tricky for the programmers. You may have a craving for spaghetti tomorrow night based on a television ad you saw earlier today, which then triggered an emotion of how enjoyable it was for you the last time you ate a bowl of pasta. Theoretically, all of the inputs could be tracked, input into a database, and then used to derive a reasonable suggestion on what to eat for dinner.
Continuing with this logic, if you were to increase the number of data points by a factor of 100,000, then the accuracy of the suggested answer should be better, but never perfect. Think of machine learning as consisting of all the techniques that enable computers to derive conclusions from the available data.
All Machine Learning is AI – but not all Artificial Intelligence is Machine Learning
When evaluating Artificial Intelligence vs. Machine Learning, it is helpful to know there are other types of Artificial Intelligence. One is natural language processing, which includes text generation, question answering, context extraction, classification, and machine translation. Speech recognition is another type of AI, which includes speech to text and text to speech. The programming involved in each of these disciplines is different but has a common theme. Each of these fields of study contributes to the appearance of intelligence, or for machines to act smart.
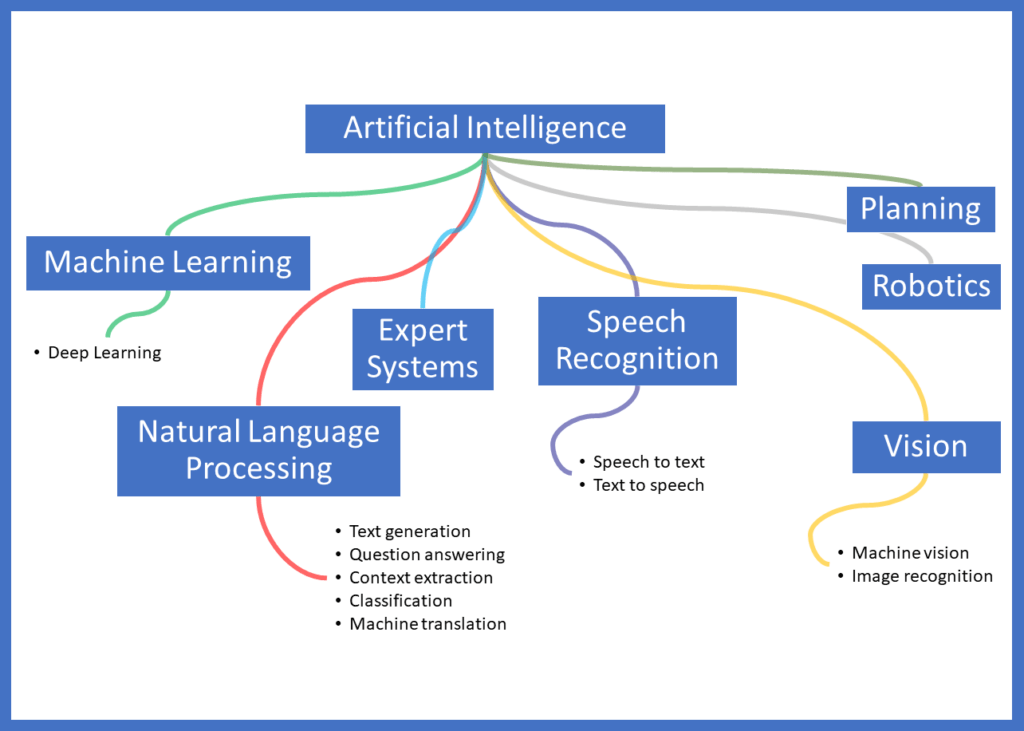
In conclusion, when defining artificial intelligence vs. machine learning, it is helpful to think of AI as being the generic term for enabling machines or automated processes to perform with greater intelligence and efficiency. Machine learning is a set of statistical algorithms that are calculated to help improve the accuracy of how data is analyzed and leveraged to make decisions.
One thing that is for sure, the field of AI is growing increasingly more sophisticated and complex every year. New breakthroughs are frequent as are new products being introduced that include this mathematical capability to unlock higher performance. One example is in the use of how automated processes are now being done smarter, through the use of Artificial Intelligence.
Read this article, How Intelligent Automation Is Driving New Productivity.
Will the future become one where machines rule the world? That is a hard question to know for sure. But, if your question is whether decisions will increasingly be made based more based on what machine learning algorithms suggest? Then that answer is highly likely.
